
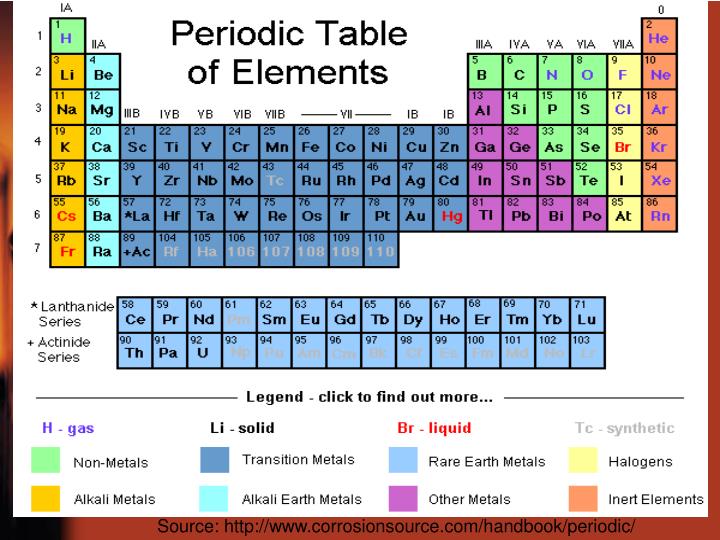
The periodic table, the great classificatory scheme of chemistry, is based on two of the most fundamental concepts in physical science-elements and atoms. Henze, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003 I.A Elementary and Atomic Concepts When discussing the putative reduction of the periodic table to modern physical theories, it is worth recalling that historically speaking it is the periodic table that led directly to many developments in modern physics. If the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, as they were initially, approximate chemical similarities occur after various regular intervals. The idea of chemical periodicity is deceptively simple. The periodic law, which underlies the periodic table, represents one of the big ideas in chemistry, along with the idea of chemical bonding, with which it is intimately connected.
Unlike other sciences only chemistry possesses a single chart, the periodic table, which embodies the whole of the discipline both explicitly and implicitly given that new analogies and relationships continue to emerge from it. The periodic table is a physical representation of two more abstract notions, namely the periodic law and the periodic system, both of which are more fundamental that the familiar periodic table. The classification of the chemical elements is clear-cut as a result of the periodic table, although some disagreements still persist. The periodic table of the elements is perhaps the most natural system of classification in the whole of science. Scerri, in Philosophy of Chemistry, 2012 Publisher Summary


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
